Digital and offset printing serve as complementary tools in the printing landscape, catering to different requirements and preferences. Offset printing, with its traditional roots, excels in producing large quantities with precise color accuracy, making it ideal for high-volume publications and branding materials. On the other hand, digital printing offers flexibility and speed, ideal for smaller quantities and personalized projects.
From the intricate details of plate creation in offset printing to the direct image transfer of digital printing, each method has its way of operating. This article delves into the inner workings of both digital and offset printing, providing a comprehensive overview of how they operate and the roles they play in contemporary printing.
The Evolution of Printing Technology
Like many industries reliant on machinery, printing is deeply intertwined with technology. From the ancient Chinese woodblocks to Gutenberg's revolutionary printing press, technological advancements have continually expanded the possibilities of printing. Today, modern printing relies primarily on two key technologies: offset printing and digital printing.
Professional printing services cater to clients with diverse printing needs, utilizing both digital and offset presses to deliver exceptional results. These services have expanded as more clients seek solutions that surpass the limitations of home printers. Professional printers excel in areas such as:
Understanding the Basics
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a technique that uses large machines to transfer an image onto paper via a series of plates and rollers. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
-
Creating Print Plates: The process begins with creating print plates, which are customized for each job. These plates hold the image or text that will be printed.
-
Transfer to Intermediate Medium: The image is transferred from the print plates to a rubber blanket, which is the intermediate medium.
-
Final Transfer to Printing Surface: Finally, the image is transferred from the rubber blanket to the printing surface, ensuring a high-quality print.
Offset printing is renowned for its ability to produce sharp and clean images, making it ideal for large print runs where consistency and quality are paramount. However, this method is less flexible when it comes to small runs or customized designs due to the need for creating new plates for each change.
Digital Printing
Digital printing leverages technology similar to that found in computer printers but on a larger scale. Instead of a desktop machine, digital printers are standalone units designed for high-volume and wide-format printing. Digital printing offers several key features:
-
Direct Printing: The image is printed directly onto the material. Unlike offset printing, where the image is transferred via an intermediate medium, digital printing applies the image directly to the surface.
Digital printing excels in producing vibrant, customizable prints on demand. This flexibility makes it ideal for personalized marketing materials, small batch projects, and designs that frequently change.
Key Operational Differences
Production Volume and Cost Efficiency
Small-Run Production
Digital printing shines for small quantities, offering consistent per-unit costs regardless of volume. With minimal setup requirements, digital printing enables cost-effective production of as few as one copy, making it ideal for:
Large-Run Production
Offset printing requires significant setup but becomes increasingly cost-effective as quantities grow. The setup costs are distributed across more units, substantially lowering the per-piece price. Offset typically becomes economical at:
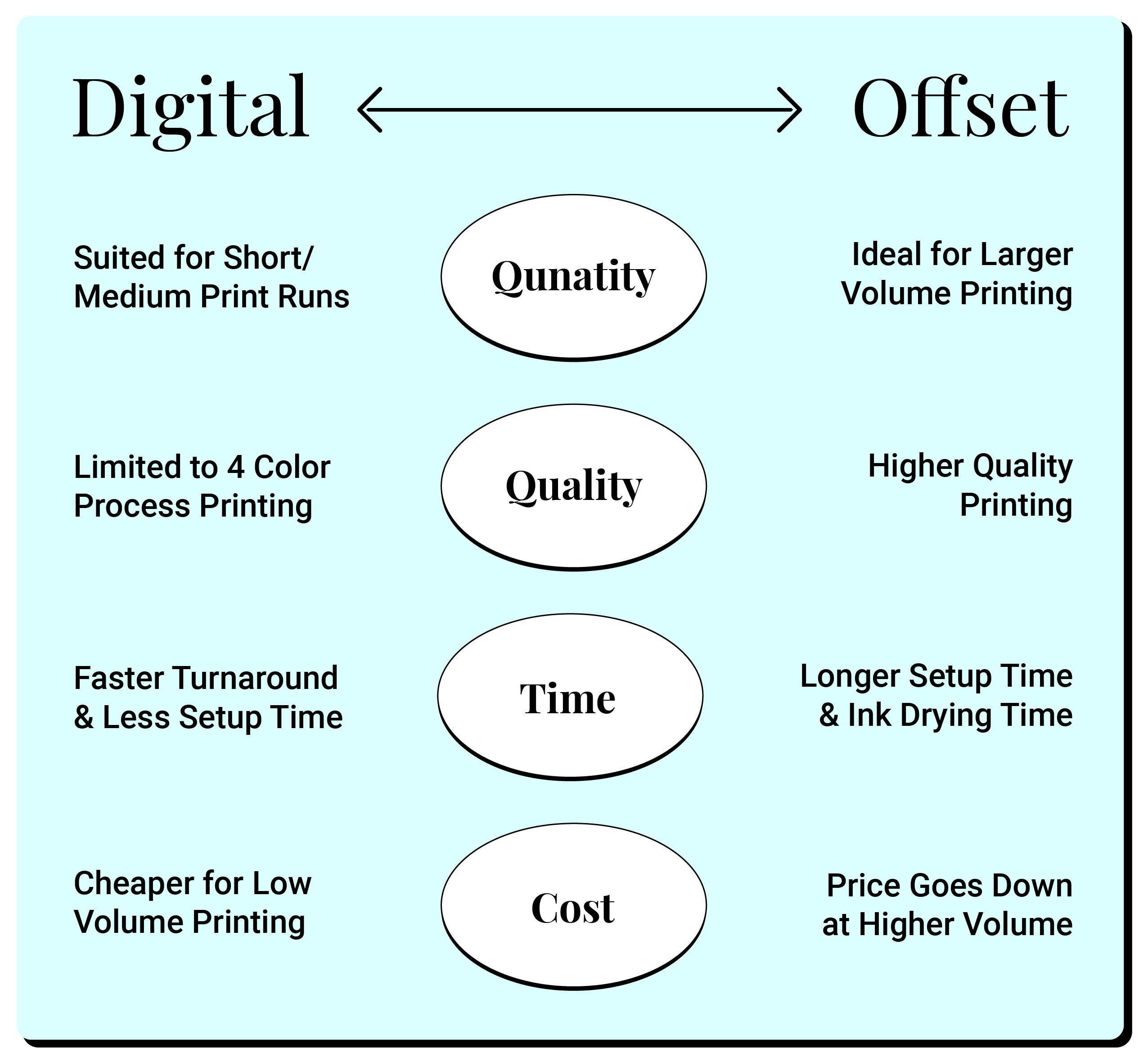
Print Quality and Color Accuracy
Digital Print Quality
Modern digital presses produce excellent results with:
However, digital printing may show slight banding in large color areas and lacks the absolute color precision of offset for brand-critical applications.
Offset Print Quality
Offset printing remains the gold standard for premium quality with:
The human-operated nature of offset presses means there can be slight variations between print runs, though they remain remarkably consistent.
Turnaround Time
Digital Production Speed
Digital printing offers quick turnaround benefits:
Offset Production Speed
Offset printing involves a longer preparation process:
However, once running, offset presses operate at high speeds, making them efficient for large volumes despite longer setup times.
Sheet Size and Format
The physical dimensions of your project can also dictate which printing method is appropriate.
Digital Printing
Offset Printing
Material Versatility
Digital Material Options
Digital printing technology has expanded to accommodate:
Material limitations exist primarily in very heavy stocks and some specialty finishes.
Offset Material Options
Offset printing excels with a wide range of materials:
The mechanical pressure of offset printing also allows for special effects like embossing when combined with additional processes.
Variable Data Capabilities
Digital Personalization
One of digital printing's greatest strengths is variable data printing:
Offset
Traditional offset printing produces identical pieces throughout the run. Variable information requires:
Final Word
Digital and offset presses each play a crucial role in the printing industry, offering distinct capabilities. Digital presses allow for quick turnaround times and the ability to print personalized materials, making them ideal for projects that require flexibility and speed. They excel in producing small to medium quantities efficiently, enabling businesses to respond rapidly to market demands.
FAQs
What is the main difference between offset and digital printing?
Offset printing is better for large quantities and precise color matching using Pantone inks. Digital printing is more cost-effective for smaller quantities and allows for variable data printing.
What is the fastest possible turnaround for digital printing?
Many print providers offer same-day service for simple digital printing projects submitted with print-ready files early in the day. Standard turnaround is typically 1-2 business days for straightforward projects.
Is paper quality different between digital and offset printing?
Both technologies can use high-quality papers, but they interact differently with the substrate. Digital printing sits more on the surface of the paper, while offset inks are absorbed more deeply. This difference is most noticeable on uncoated stocks, where offset often produces richer results.
What types of materials can be printed on with digital printing?
Digital printing can handle various materials including paper, plastic, vinyl, and canvas.
Is it possible to combine digital and offset printing in one project?
Yes, hybrid approaches are increasingly common. For example, a catalog might have its cover and standard pages printed offset for quality and economy, while incorporating digitally printed personalized inserts or variable coupons.
We at Machine Dalal have a wide selection of print, packaging, and converting machines listed with us. Industry sellers from all over the world list their print equipment with us to reach interested buyers who regularly visit our platform to find equipment that matches their needs.
At Machine Dalal, we connect the supply and purchasing needs of the print industry.
Check out our apps on
Android or
iOS smartphone.